As How to Identify 20 Different Types of Birds takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original. Exploring the diverse avian world can be a fascinating journey filled with surprises and discoveries.
Introduction to Bird Identification

Bird identification is essential for understanding the diverse avian species that inhabit our environment. By being able to identify different types of birds, individuals can gain a deeper appreciation for the natural world around them.
Knowing how to identify various bird species can also provide valuable information about the health of ecosystems, as certain birds are indicators of environmental changes. Birdwatching enthusiasts can enhance their experience by recognizing different bird types, allowing them to track migrations, observe behavior patterns, and contribute to citizen science efforts.
Understanding Bird Characteristics
When it comes to identifying different types of birds, understanding key physical characteristics is essential. These characteristics include size, shape, color, markings, beak shape, and behavior, all of which can help differentiate bird species from one another.
Size
Size is an important characteristic to consider when identifying birds. Some species are small and delicate, while others are large and robust. For example, hummingbirds are known for their tiny size, while eagles are recognized for their impressive wingspan.
Shape
The shape of a bird’s body, wings, and tail can also vary greatly among different species. For instance, the streamlined body of a swift allows it to soar effortlessly through the air, while the long, pointed wings of a falcon help it achieve high speeds during flight.
Color and Markings
Color and markings play a significant role in bird identification. Some birds have vibrant plumage with distinct patterns, like the bright red of a cardinal or the intricate spots of a woodpecker. On the other hand, certain species may have more subtle coloring to blend in with their surroundings, such as the camouflaged feathers of an owl.
Beak Shape
The shape of a bird’s beak is adapted to its diet and feeding habits. Birds with long, slender beaks like hummingbirds are often nectar feeders, while those with hooked beaks like raptors are skilled hunters. For example, the thick, sturdy beak of a finch is ideal for cracking open seeds.
Behavior
Bird behavior can also aid in identification. Some species are known for their distinctive calls or songs, while others have unique feeding or nesting habits. Observing how a bird interacts with its environment can provide valuable clues for identification.
Identifying Common Backyard Birds
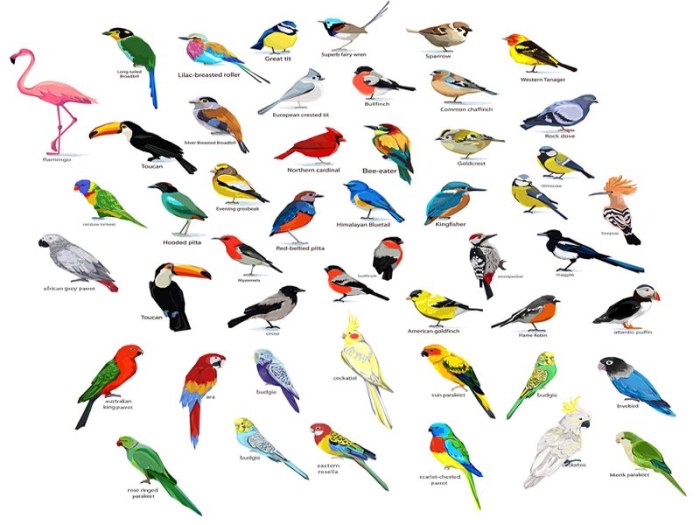
Common backyard birds are a delight to observe and attract with the right environment. Here are some popular species you might encounter:
Sparrows
Sparrows are small, brown birds with streaked plumage. They are often found in bushes, shrubs, and grassy areas. Sparrows feed on seeds, grains, and insects.
Robins
Robins are medium-sized birds with a red breast and brownish-gray back. They are commonly seen hopping on lawns and gardens, searching for worms and insects to eat.
Cardinals
Cardinals are easily recognizable due to their bright red plumage and distinctive crest. They prefer shrubby areas and feed on seeds and fruits. Cardinals are known for their beautiful songs.
Blue Jays
Blue Jays are striking birds with blue and white plumage, along with a crest on their heads. They are often found in forests, parks, and backyards. Blue Jays are omnivorous, eating nuts, seeds, insects, and even small vertebrates.
To attract these common backyard birds, consider providing bird feeders with appropriate seeds and nuts. Adding birdbaths and planting native shrubs and trees can also create a welcoming environment for these species. Remember to keep feeders clean and refill them regularly to maintain the birds’ interest. Set up a comfortable place for observation, such as a bird-watching station near a window or in the garden, to enjoy watching these feathered visitors.
Identifying Waterfowl

When it comes to identifying waterfowl, it’s important to familiarize yourself with different types such as ducks, geese, swans, and herons. Each of these species has unique characteristics that can help you distinguish one from the other.To recognize waterfowl, pay attention to their size, shape, plumage, and habitat. Ducks, for example, are usually smaller with a rounded body and webbed feet, while geese are larger with a longer neck and distinctive honking sound.
Swans are known for their long necks and graceful appearance, often found in bodies of water like lakes and ponds. Herons, on the other hand, have long legs and necks, with a slow and deliberate hunting style near water sources.
Distinct Behaviors and Characteristics
- Waterfowl can often be identified by their feeding habits – ducks may dabble in shallow water for food, while herons stand still waiting to catch fish.
- Geese are known for their V-shaped flight formations during migration, making loud calls as they travel long distances.
- Swans are graceful swimmers, gliding across the water with elegance and beauty.
- Herons are skilled hunters, using their sharp bills to catch prey with precision.
Recognizing Birds of Prey
Birds of prey, also known as raptors, are a fascinating group of birds that are known for their hunting skills and distinctive physical features.
Characteristics of Birds of Prey
- Birds of prey have sharp, curved talons and strong, hooked beaks that are used for catching and tearing apart prey.
- They have exceptional eyesight, allowing them to spot prey from great distances.
- Raptors have powerful wings and are known for their swift and agile flight patterns.
Differentiating Raptors
- Eagles are known for their large size and impressive wingspan, often soaring high in the sky.
- Hawks are smaller than eagles and can be seen gliding in circles as they hunt for prey.
- Falcons are known for their incredible speed and agility, often diving down to catch their prey in mid-flight.
- Owls are nocturnal hunters with silent flight, thanks to their specialized feathers that reduce noise.
Interesting Facts about Birds of Prey
- Raptors have excellent hunting skills and are known for their ability to take down prey much larger than themselves.
- Many birds of prey exhibit strong territorial behavior, fiercely defending their nesting sites from intruders.
- Some species of raptors, like the Osprey, have unique hunting techniques, such as plunging feet-first into the water to catch fish.
Identifying Songbirds
Songbirds are known for their melodious calls and diverse appearances, making them a popular group of birds to identify. They can be found in a variety of habitats, from forests to urban areas, and are known for their beautiful songs. Some common examples of songbirds include warblers, thrushes, finches, and sparrows.
Identifying Songbirds by Their Unique Characteristics
Songbirds can be identified by a combination of their unique songs, plumage, and nesting habits. Each species of songbird has its own distinct song, which can be used to differentiate them from one another. Additionally, their plumage, or feathers, can vary greatly in color and pattern, providing further clues to their identity. Observing their nesting habits, such as where they build their nests and what materials they use, can also help in identifying these birds.
- Warblers: Known for their vibrant colors and intricate songs, warblers are often found in trees and shrubs.
- Thrushes: These birds have spotted or speckled breasts and are known for their clear, flute-like songs.
- Finches: Finches come in a variety of colors and are often seen at bird feeders, where they enjoy seeds.
- Sparrows: Sparrows are small, brown birds with distinctive markings on their heads and chests and are commonly found in urban areas.
Recognizing Shorebirds: How To Identify 20 Different Types Of Birds

Shorebirds are a diverse group of birds commonly found along coastlines, marshes, and wetlands. They have adapted to thrive in these habitats and often display unique physical characteristics and behaviors.Some common shorebirds include sandpipers, plovers, and herons. Sandpipers are known for their long, slender bills used for probing in the sand for food. Plovers, on the other hand, have shorter bills and are often seen running along the shoreline in search of prey.
Herons are larger shorebirds with long legs and necks, commonly found wading in shallow water to catch fish.To spot and identify shorebirds, pay attention to their feeding habits and habitats. Sandpipers, for example, can be found feeding on insects and small crustaceans along the shoreline. Plovers may be seen running in and out of the water to catch small fish or crustaceans.
Herons prefer to wade in shallow water, patiently waiting for fish to come within striking distance.
Identifying Sandpipers
- Sandpipers have long, slender bills for probing in the sand.
- They feed on insects and small crustaceans along the shoreline.
- Look for sandpipers with a distinctive bobbing motion as they search for food.
Spotting Plovers, How to Identify 20 Different Types of Birds
- Plovers have shorter bills and are often seen running along the shoreline.
- They feed on small fish and crustaceans by running in and out of the water.
- Watch for plovers with a quick, darting movement as they hunt for prey.
Observing Herons
- Herons are larger shorebirds with long legs and necks.
- They wade in shallow water, waiting patiently for fish to catch.
- Look for herons standing motionless or moving slowly in the water.
Identifying Birds by Habitat
When it comes to identifying birds by habitat, it is essential to understand how different bird species are adapted to various environments. Birds have unique characteristics that allow them to thrive in specific habitats such as forests, grasslands, wetlands, and urban areas. By recognizing these adaptations, birdwatchers can easily pinpoint different bird species based on their preferred habitats.
Forests
In forested areas, you may come across birds like the Woodpecker, Warbler, and Owl. These birds have special adaptations such as strong beaks for pecking on trees, camouflage plumage for blending in with the surroundings, and keen eyesight for hunting in low light conditions.
Grasslands
Birds commonly found in grasslands include the Meadowlark, Sparrow, and Hawk. These birds have adaptations like long legs for walking through tall grass, sharp talons for catching prey on the ground, and streamlined bodies for efficient flight over open fields.
Wetlands
In wetland areas, you may spot birds like the Heron, Duck, and Egret. These birds have adaptations such as long necks for reaching into the water, webbed feet for swimming, and waterproof feathers for staying dry while hunting for food in marshy areas.
Urban Areas
Birds that thrive in urban environments include the Pigeon, Sparrow, and Crow. These birds have adapted to city life by scavenging for food scraps, nesting in buildings, and navigating through crowded spaces with ease.
Conclusion

In conclusion, mastering the art of identifying different bird species opens up a whole new dimension to nature exploration. With practice and keen observation, birdwatching can evolve into a rewarding and enriching hobby, allowing you to truly appreciate the beauty and diversity of our feathered friends.