How to Learn 5 Different Types of Clouds invites you to explore the fascinating world of cloud formations, from their classification to photography techniques, providing a comprehensive guide to enhancing your cloud knowledge.
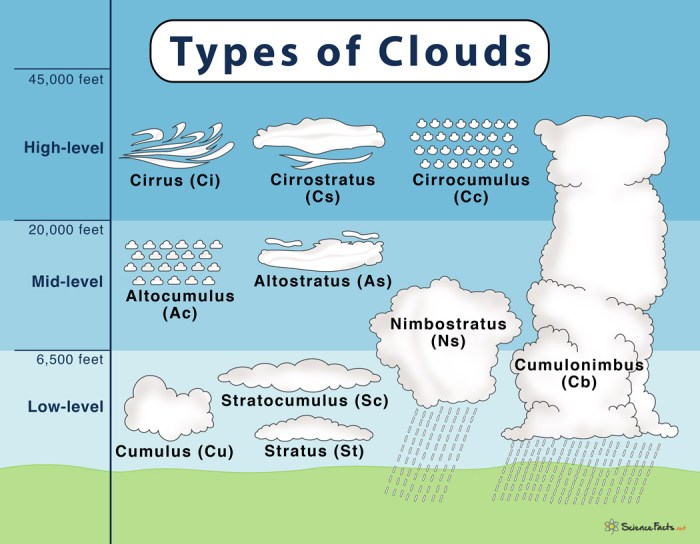
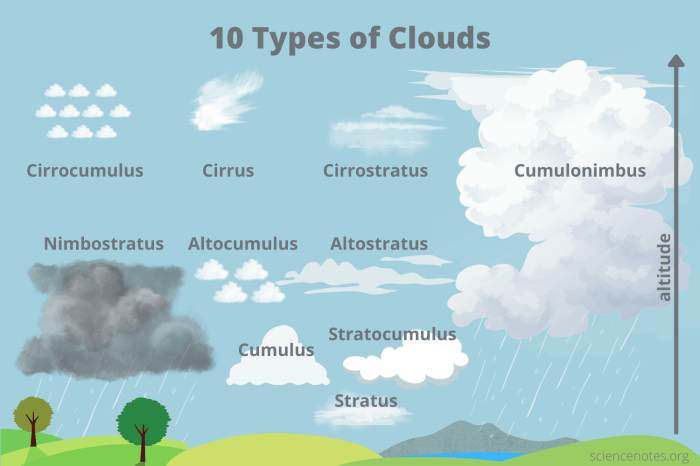
Types of Clouds
Clouds play a crucial role in the Earth’s atmosphere, and there are five main types of clouds that can be identified based on their distinct characteristics and formations. Let’s explore each type in detail.
Cirrus Clouds
Cirrus clouds are high-altitude clouds that are thin, wispy, and feathery in appearance. They are composed of ice crystals and are commonly found at elevations above 20,000 feet. Cirrus clouds are often associated with fair weather, but they can also indicate the approach of a warm front.
Cumulus Clouds
Cumulus clouds are fluffy, white clouds with flat bases and rounded tops. They typically develop in fair weather conditions but can grow into larger storm clouds known as cumulonimbus clouds. Cumulus clouds are commonly seen during the day and are a familiar sight in the sky.
Stratus Clouds
Stratus clouds are low-level clouds that form in layers or sheets covering the sky. They are often gray or white in color and can bring overcast conditions and light precipitation. Stratus clouds are associated with stable atmospheric conditions and can linger for long periods.
Nimbus Clouds
Nimbus clouds, also known as rain clouds, are dark, dense clouds that bring precipitation. These clouds can be of various types, such as nimbostratus or cumulonimbus clouds, and are responsible for producing rain, snow, or hail. Nimbus clouds are a sign of approaching inclement weather.
Stratocumulus Clouds
Stratocumulus clouds are low-level clouds that appear as a combination of stratus and cumulus clouds. They form in a layered or lumpy pattern and can cover large areas of the sky. Stratocumulus clouds are often seen during fair weather conditions but can also indicate the possibility of light precipitation.
Formation of Clouds

Clouds are formed in the atmosphere through a process that involves the interaction of water vapor, condensation, and evaporation. When water evaporates from bodies of water or moist surfaces, it rises into the atmosphere as invisible water vapor. As the warm, moist air rises, it cools down at higher altitudes, leading to condensation of the water vapor into tiny water droplets or ice crystals.
These tiny droplets and crystals then come together to form visible clouds.
Role of Condensation and Evaporation
Condensation plays a crucial role in cloud formation as it involves the transformation of water vapor into liquid water droplets or ice crystals. This process occurs when the air cools down, causing the water vapor to change state. On the other hand, evaporation is the process by which water on the Earth’s surface is transformed into water vapor and rises into the atmosphere, initiating the cloud formation process.
- Condensation leads to the formation of cloud droplets or ice crystals from water vapor.
- Evaporation is responsible for transferring water from the Earth’s surface into the atmosphere.
Process of Cloud Formation
The process of cloud formation begins with the evaporation of water from the Earth’s surface, which leads to the rise of warm, moist air. As this air ascends, it cools down, causing condensation of water vapor into tiny droplets or crystals. These particles then come together to form clouds, which are visible collections of water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air.
- Evaporation of water from the Earth’s surface.
- Rise of warm, moist air into the atmosphere.
- Condensation of water vapor into cloud droplets or ice crystals.
- Formation of visible clouds through the aggregation of these particles.
Environmental Conditions for Cloud Formation, How to Learn 5 Different Types of Clouds
Several environmental conditions contribute to the formation of clouds, including humidity levels, temperature, and air pressure. For instance, high humidity levels increase the amount of water vapor in the air, making it more likely for condensation and cloud formation to occur. Additionally, temperature changes in the atmosphere play a crucial role in determining the altitude at which clouds form and the type of clouds that develop.
- High humidity levels promote the condensation of water vapor into clouds.
- Temperature changes influence the altitude and type of clouds that form.
- Air pressure variations can impact the formation and movement of clouds in the atmosphere.
Identifying Clouds
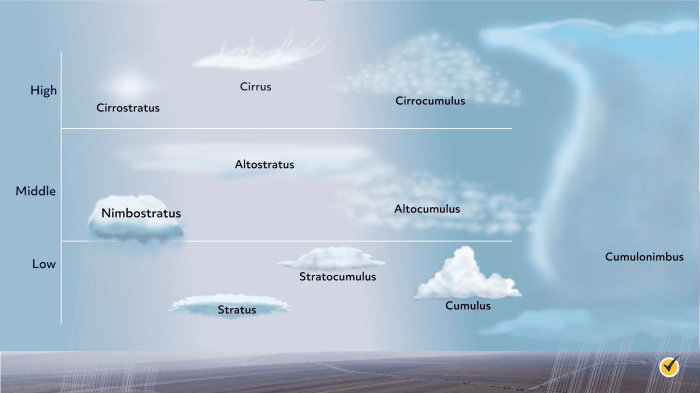
Identifying different types of clouds can be an exciting and rewarding skill for any weather enthusiast. By observing key features and characteristics, you can distinguish between various cloud types and enhance your understanding of the atmosphere.When identifying clouds, it is essential to look for specific attributes such as shape, color, altitude, and texture. These features can help you differentiate between cloud types and classify them accurately.
Additionally, observing the movement and behavior of clouds can provide valuable clues about their classification.
Techniques for Cloud Identification
- Learn about the different cloud categories, including cirrus, cumulus, stratus, and nimbus clouds.
- Observe the shape and structure of the clouds to determine their type (e.g., wispy cirrus clouds vs. fluffy cumulus clouds).
- Take note of the cloud’s altitude in the sky, as this can indicate the type of cloud it is (e.g., high-altitude cirrostratus vs. low-altitude cumulonimbus).
- Pay attention to the color of the clouds, as certain hues can be characteristic of specific cloud types (e.g., dark gray nimbostratus clouds indicating rain).
Remember to practice regularly and observe clouds in various weather conditions to sharpen your cloud identification skills.
Cloud Classification Systems: How To Learn 5 Different Types Of Clouds
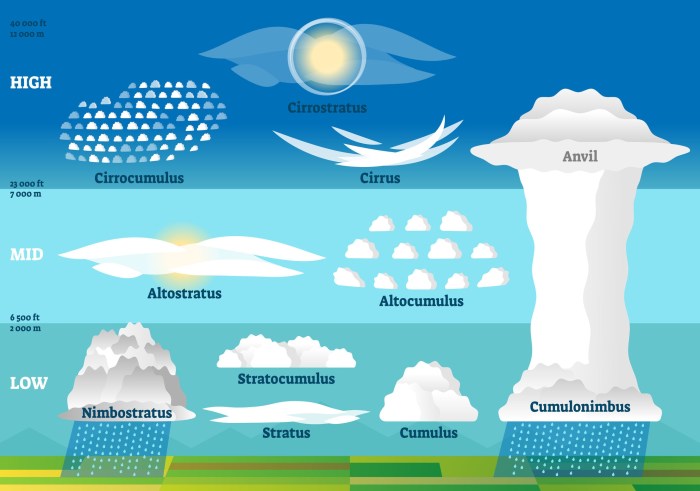
Cloud classification systems are used in meteorology to categorize different types of clouds based on their appearance and altitude in the atmosphere. By classifying clouds, meteorologists can better understand weather patterns and make more accurate forecasts. There are several cloud classification systems used worldwide, with the most common being the International Cloud Atlas classification system established by the World Meteorological Organization.
Importance of Cloud Classification in Meteorology
Cloud classification is essential in meteorology as it helps meteorologists identify specific cloud types and their associated weather patterns. By understanding the characteristics of different cloud types, meteorologists can predict the likelihood of precipitation, storms, or other weather events. This information is crucial for issuing weather warnings and advisories to the public, helping to mitigate the impact of severe weather events.
- Cloud classification allows meteorologists to track the movement and development of clouds, aiding in the interpretation of weather conditions.
- By categorizing clouds, meteorologists can analyze atmospheric stability, humidity levels, and other factors that influence weather formation.
- Understanding cloud classification helps in studying climate change and its effects on cloud formation and distribution.
Comparison of Different Cloud Classification Systems
The International Cloud Atlas classification system is the most widely used system for cloud classification, dividing clouds into genera, species, and varieties based on their appearance and altitude. Other classification systems, such as the Luke Howard cloud classification system, focus on cloud shapes and patterns to categorize clouds.
Cloud classification systems like the International Cloud Atlas provide a standardized way for meteorologists around the world to communicate and record cloud observations.
Role of Cloud Classification in Weather Forecasting
Cloud classification plays a crucial role in weather forecasting by providing valuable information about upcoming weather conditions. Meteorologists can use cloud classification data to predict the likelihood of precipitation, thunderstorms, or other weather events based on the characteristics of specific cloud types.
- For example, cumulonimbus clouds are associated with thunderstorms and heavy rainfall, making them indicators of severe weather conditions.
- Stratus clouds often bring overcast skies and light drizzle, indicating stable atmospheric conditions with a lower chance of precipitation.
Cloud Photography
Capturing stunning cloud photos can be a rewarding experience for photography enthusiasts. The sky offers a canvas of ever-changing shapes, colors, and patterns that can create breathtaking images. To make the most of your cloud photography, consider the following tips and techniques.
Equipment and Settings
When it comes to cloud photography, having the right equipment and settings can make a significant difference in the quality of your photos. Here are some recommendations:
- Use a DSLR or mirrorless camera with a high-resolution sensor to capture detailed cloud formations.
- Opt for a wide-angle lens to include more of the sky in your frame and emphasize the vastness of the clouds.
- Set your camera to manual mode to have full control over settings such as aperture, shutter speed, and ISO.
- Adjust your aperture to achieve the desired depth of field, keeping the entire scene in focus.
- Experiment with different shutter speeds to capture the movement of clouds, from wispy streaks to dramatic billows.
- Keep your ISO low to maintain image quality and reduce noise in your photos.
Composing Cloud Photos
Composition plays a crucial role in creating visually appealing cloud photos. Consider the following creative ideas:
- Position the clouds in the frame using the rule of thirds to create a balanced composition.
- Include other elements such as landscapes or silhouettes to add interest and scale to your cloud photos.
- Experiment with different perspectives and angles to find unique compositions that highlight the beauty of the clouds.
- Use leading lines or patterns in the sky to draw the viewer’s eye towards the focal point of your photo.
Lighting and Angles
Lighting and angles can greatly impact the mood and atmosphere of your cloud photos. Here’s how you can use them to enhance your photography:
- Shoot during golden hour or blue hour to capture warm, soft light that adds a magical quality to your cloud photos.
- Experiment with backlighting to create silhouettes of clouds or capture the glowing edges of cumulus clouds.
- Consider shooting from different angles, such as low to the ground or from a high vantage point, to add depth and dimension to your cloud photos.
- Pay attention to the direction of light and shadows cast by the clouds to create dynamic and visually striking compositions.
Conclusive Thoughts
Delve into the realm of clouds with the knowledge gained from How to Learn 5 Different Types of Clouds, where you can now confidently identify, classify, and capture the beauty of these natural phenomena.