How to Predict the Weather opens up a world of fascinating insights into the intricate art of weather forecasting. From unraveling the basics to exploring advanced tools, get ready for an enlightening journey.
Understanding Weather Prediction

Weather prediction involves analyzing atmospheric conditions to forecast how the weather will change over time. Meteorologists use various tools and data to predict factors such as temperature, precipitation, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure.Accurate weather prediction is crucial for a variety of reasons. It helps individuals and communities prepare for extreme weather events such as hurricanes, blizzards, or heatwaves. Farmers rely on weather forecasts to plan their planting and harvesting schedules, while airlines use predictions to ensure safe travel routes and avoid turbulence.
Impact on Daily Life
- Planning outdoor activities: People use weather forecasts to plan events like picnics, beach trips, or outdoor sports based on expected conditions.
- Choosing clothing: Knowing the weather forecast helps individuals dress appropriately for the day, whether it’s sunny, rainy, or cold.
- Traffic and commuting: Weather predictions influence traffic patterns and commuting times, especially during severe weather conditions like snowstorms or heavy rain.
- Energy consumption: Utility companies use weather forecasts to anticipate demand for heating or cooling, adjusting energy production accordingly.
Factors Affecting Weather Prediction
Weather prediction is influenced by several key factors that contribute to the accuracy of forecasts. These factors range from technological advancements to geographical elements that impact the overall understanding of weather patterns.
Role of Technology in Enhancing Weather Prediction Accuracy
Advancements in technology have significantly improved the accuracy of weather prediction. The use of satellites, radar systems, computer models, and weather stations provides meteorologists with real-time data that helps in analyzing and forecasting weather conditions. These technological tools allow for better monitoring of atmospheric changes, leading to more precise predictions of weather patterns.
Geography and Topography in Weather Prediction
Geography and topography play a crucial role in predicting weather due to their influence on local climates. The layout of landforms, bodies of water, and elevation levels can impact wind patterns, temperature variations, and precipitation levels in a specific region. Understanding these geographical features helps meteorologists anticipate how weather systems will behave in different areas, leading to more accurate forecasts.
Meteorological Instruments and Tools: How To Predict The Weather

Meteorologists rely on a variety of instruments and tools to accurately predict the weather. These tools help gather data on atmospheric conditions, which is crucial for making informed forecasts.
Common Instruments Used in Weather Prediction
- Anemometer: Measures wind speed and direction, providing valuable information on upcoming weather patterns.
- Barometer: Measures atmospheric pressure, which can indicate changes in weather conditions such as approaching storms or clear skies.
- Hygrometer: Measures humidity in the air, aiding in predicting precipitation and fog formation.
- Thermometer: Measures temperature, a key factor in determining weather patterns and trends.
- Rain Gauge: Collects and measures the amount of precipitation, helping forecast rainfall and snowfall.
How Each Instrument Helps in Forecasting Weather, How to Predict the Weather
- Anemometer: Wind direction and speed data from anemometers help meteorologists understand how weather systems are moving and predict storm patterns.
- Barometer: Changes in atmospheric pressure measured by barometers can indicate the approach of high or low-pressure systems, which are linked to specific weather conditions.
- Hygrometer: By monitoring humidity levels, hygrometers assist in predicting the likelihood of precipitation, fog, or dry weather conditions.
- Thermometer: Temperature readings are crucial for determining the type of weather to expect, whether it’s warm and sunny or cold and snowy.
- Rain Gauge: Precipitation data collected by rain gauges helps meteorologists forecast rain or snow events accurately, aiding in flood prevention and drought prediction.
Comparison of Traditional Tools with Modern Technological Advancements
- Traditional Tools: Manual instruments like barometers and thermometers have been used for centuries and are still reliable in providing accurate weather data. However, they require human observation and recording, which can be time-consuming.
- Modern Technological Advancements: Automated weather stations equipped with advanced sensors and satellite technology can collect real-time data on a larger scale and transmit it instantly to meteorologists. This allows for more precise and timely weather forecasts, improving overall accuracy and efficiency in weather prediction.
Weather Forecasting Methods

Weather forecasting involves various methods to predict future weather conditions. Each method has its own accuracy and limitations, impacting the reliability of weather predictions. Here, we will explore different methods used in weather forecasting and discuss their accuracy and limitations.
Satellite Imagery
Satellite imagery is a crucial method in weather forecasting, providing a bird’s eye view of weather patterns. By analyzing cloud formations, temperature gradients, and wind movements captured by satellites, meteorologists can predict weather changes accurately. However, satellite imagery may not always capture small-scale weather events, leading to limitations in predicting localized weather conditions.
Computer Models
Computer models use complex algorithms to simulate and predict weather patterns based on current atmospheric data. These models consider various factors like temperature, pressure, humidity, and wind speed to forecast future weather conditions. While computer models offer detailed predictions, they may sometimes produce inaccuracies due to uncertainties in input data or limitations in the model’s algorithms.
Doppler Radar
Doppler radar is used to track precipitation, storm movement, and severe weather events in real-time. By analyzing radar data, meteorologists can issue warnings and predict the intensity and path of storms accurately. However, Doppler radar has limitations in predicting non-precipitation related weather phenomena like fog or temperature changes.
Weather Stations
Weather stations across the globe collect real-time data on temperature, humidity, wind speed, and atmospheric pressure. This data is crucial for monitoring current weather conditions and making short-term forecasts. While weather stations provide accurate localized data, their coverage may be limited, impacting the accuracy of long-term weather predictions.
Interpretation of Weather Data
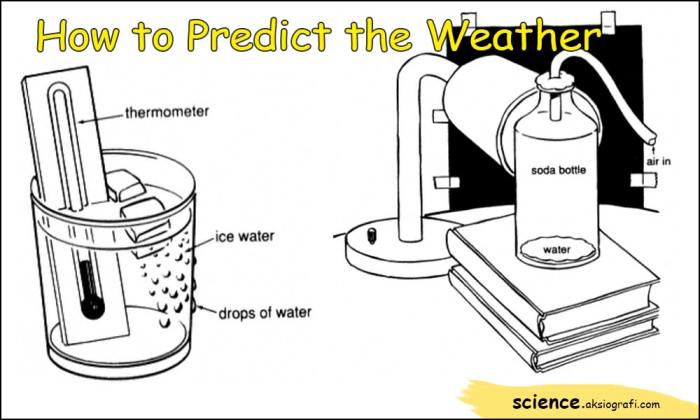
Meteorologists rely on a variety of data sources to interpret and predict the weather accurately. This involves analyzing data from satellites, radars, and historical records to make informed forecasts.
Analysis of Satellite Data
Satellites provide essential information about cloud cover, temperature patterns, and atmospheric conditions. Meteorologists analyze satellite images to track weather systems, such as storms, and monitor their movement and intensity.
Interpretation of Radar Data
Radar data helps meteorologists detect precipitation, such as rain, snow, or hail, in real-time. By interpreting radar images, meteorologists can anticipate the timing and location of incoming weather events with greater accuracy.
Significance of Historical Weather Data
Historical weather data is crucial for making future predictions. By studying past weather patterns and events, meteorologists can identify trends and recurring phenomena that influence the weather. This historical context provides valuable insights for forecasting upcoming weather conditions.
Outcome Summary

As we wrap up our discussion on How to Predict the Weather, it’s evident that weather forecasting is a blend of science and technology crucial for our daily lives. Stay tuned for more exciting updates on this dynamic field.